WAEC GCE Economics Answers 2023 Questions Released.
The Waec gce economics answers 2023 exam questions have been released here. The West African Examination Council (WAEC) Economics paper for SSCE will be written on Saturday, 3rd December 2023.
The Waec Gce Economics objective answers to questions 2023 and Essay question paper will arrive and the exam commences by 8:30 am which will last for 2hrs while the Economics waec objective question paper exam will commence 10:30 am to last 1hr. Read the test questions below.
In this post, we will be giving out samples of waec economics questions for candidates that will participate in the examination from past questions. There is nothing like Waec economics expo 2023 online.
WAEC GCE Economics Answers 2023 Questions.
PAPER 2 [Essay]
Answer any FIVE questions.
Write your answers in the answer booklet provided.
1. (a) Distinguish between small-scale production and large-scale production.
(b) Describe any five internal economies of large-scale production.
ANS: (a) Small-scale production is a production with the small capital outlay and therefore at a low level of output. On the other hand, large-scale production is a production with a large-scale outlay and therefore results in a high level of output.
(b) Some of the internal economies of large-scale production are:
(i) Technical economies: a large firm has the advantage in the use of factor inputs which results in lower cost per unit of output.
(ii) Financial economies: a large-scale producer can borrow money from a financial institutions at a lower rate because it can offer better collateral security.
(iii) Marketing economies: a large firm can buy inputs in bulk and possibly at discounts. It can also pay less on transportation and advertisement which result in lower operating cost.
(iv) Managerial economies: when output is increasing managerial cost increases at a slower rate. The number of managerial staff may increase with output. OR as output increases, specialists can be employed to take charge of the various processes e.g. marketing.
(v) Risk-bearing economies: a large firm is able to bear losses arising from its operations as it can provide insurance coverage. OR It can also diversify its product and its market.
(vi) Welfare economies: a large firm can provide better conditions of service which may enhance the level of productivity and also attract highly skilled manpower.
(vii) Research economies: a large firm can invest a huge amount in research and thereby experience technical progress.
2. A village consists of twenty (20) households with the following annual incomes:
|
(Incomes N) |
||||
|
30 |
20 |
50 |
40 |
60 |
|
40 |
40 |
50 |
20 |
60 |
|
80 |
40 |
20 |
20 |
70 |
|
40 |
70 |
30 |
40 |
80 |
(a) Determine the (i) mean income;
(ii) modal income;
(iii) median income.
(b) What is the range of the income distribution?
(c) Calculate the total tax that could be generated from the village if
(i) a flat-rate tax of 7% is imposed on all households;
(ii) a flat-rate tax of 15% is imposed on all households earning N4,000 per annum and above.
3. (a) Why is scarcity a fundamental problem in Economics?
(b) Give a reason why Economics is a;
(i) Science;
(ii) Social Science.
ANS: (a) Economics seeks to study the relationship between ends and means. Ends are unlimited while the means are limited. Scarcity means resources are limited in relation to the ends. Economics is therefore concerned with allocating the limited resources among competing and unlimited wants.
(b) (i) Economics is a science because it adopts the scientific method.
(ii) Economics is a social science because it studies human behaviour. e.g. If the price of a commodity rises, people will buy less, other things equal.
4. (a) Differentiate between direct and indirect taxation.
(b) Highlight any five advantages of indirect taxation to developing countries.
ANS: (a) Direct taxation refers to taxes on income and properties of individuals and organizations e.g. personal income tax, profit tax.
On the other hand, indirect tax refers to taxes on goods and services e.g. excise duties, custom duties, etc.
(b) (i) In developing countries where incomes are generally low, indirect taxes yield more revenue to the government.
(ii) Where unemployment is high, indirect taxes yield more revenue.
(iii) It is cheap and easy to collect, e.g. custom duties.
(iv) It has a wider coverage than direct tax.
(v) It is not easy to evade. Consumers pay as they consume the commodities.
(vi) It is not a disincentive to work.
(vii) It is used to discourage consumption of harmful goods.
(viii) It is used to protect infant industries.
(ix) It is used to correct balance of payments deficit.
(x) It is used to prevent dumping.
5. (a) Define labour.
(b) Give four factors that affect the efficiency of labour in your country.
ANS: (b) (i) Education and Training: All kinds of labour require training which may include formal training, training on the job.
(ii) Availability of equipment and tools: Labour efficiency also depends on the equipment and tools available to workers.
(iii) Physical Environment: The environment in which labour works helps to determine its efficiency as well as its productivity e.g. harsh physical environment.
(iv) Human environment – conducive management style will increase labour efficiency.
6. (a) Define money.
(b) State the three motives for holding money.
(c) Mention two determinants of each of the motives for holding money.
ANS: Transactions motive
(i) size of income;
(ii) the interval between wage payments;
(iii) availability of credit;
(iv) family size.
Precautionary motive
(i) size of income;
(ii) the interval between wage payments;
(iii) availability of credit;
(iv) perception of risks.
Speculative motive
(i) the rate of interest;
(ii) the degree of risk aversion.
7. (a) With the aid of a diagram, explain a minimum price.
(b) State any five measures by which a minimum price for agricultural products can be made effective.
8. (a) What is a supply schedule?
(b) Using an example, show how a market supply schedule of a product is obtained from individual supply schedules.
(c) State three examples of exceptional demand.
ANS: (c) Exceptional demand:
i. Fixed demand or perfectly inelastic demand e.g. salt
ii. Perfectly elastic demand
iii. Expectation of future increase in price.
iv. Articles of ostentation.
v. Giffen goods.
9. (a) With examples, distinguish between direct and indirect tax.
(b) Explain any four problems of tax collection in any West African Country.
ANS: (a) A direct tax is a tax on incomes and properties. Examples include personal income tax, company tax, death duties, inheritance tax, capital gains taxes, etc.
Whereas, an indirect tax is a tax on goods and services. Examples include sales tax, import and export duties, excise tax, purchase tax, value-added tax, etc.
(b) (i) absence of reliable records of business activities and revenues collected.
(ii) the prevalence of subsistence production.
(iii) corruption on the part of tax officials.
(iv) high level of tax evasion and tax avoidance etc.
10. (a) What is the demographic transition theory?
(b) Explain the three stages of the theory.
ANS: (a) Demographic Transition Theory is concerned with the historical population growth of society. It explains the relationship between fertility and mortality on population growth and how developed countries in contemporary times have passed through three identical stages of population history.
(b) Stages of the Theory;
stage 1 (pre-transition phase/ stage)
stage 2 (transition phase/ stage)
stage 3 (post transition phase /stage)
11. (a) Differentiate between shares and debentures.
(b) Identify any four problems encountered by farmers in raising capital
ANS: (a) A share is the smallest unit into which the capital of a company is divided. It is a unit of ownership of a business concern while a debenture is a loan capital or corporate bond. A debenture holder is a creditor to a company.
(b) (i) low level of loanable funds;
(ii) the inability of firms to produce the required collateral facilities;
(iii) under-developed money and capital markets;
(iv) the high cost of loans;
(v) the fluctuation of share prices;
(vi) Government financial regulation.
12. (a) What is a Capital market?
(b) Describe any three instruments used in the capital market.
ANS: (a) The capital market is a financial market in which funds for medium and long term investments are borrowed or lent.
(b) (i) Shares: These are financial instruments utilized in the capital market for long term investments. A share is the portion of a limited liability company owned by an investor.
(ii) Bonds: This is a long term financial security used to source for funds. Bonds may be issued by firms, financial institutions or governments. Bonds issued by the government are generally regarded as very safe.
(iii) Treasury certificates: These are government financial securities that mature after a year. They are issued by the government through the central bank to either borrow or lend money in the capital market.
WAEC GCE Economics Obj Answers 2023 Questions.
PAPER 1 [Objective]
Answer ALL questions in this section.
Shade your answers on the answer booklet provided.
1. Scarcity in economics means that _______
A. human wants are limitless
B. the economy has very few resources
C. the economy can scarcely produce anything
D. resources are limited.
2. Air is essential to life but commands no price! But Diamond is not essential to life but commands a high price! This is the paradox of ______
A. thrift B. value C. abundance D. scarcity.
3. Economics of scale operate only when ______
A. marginal cost is falling with input
B. average cost is falling with input
C. fixed cost is variable
D. variable cost is less than the fixed cost.
4. Efficiency in production involves _______
A. reducing the size of the workforce
B. producing a given output with the lowest cost combination of factors of production
D. increasing the quantity of the fixed factor of production.
5. An effect of inflation is that it ___________
A. discourages trade by barter
B. favours debtors at the expense of creditors
C. increases the real income of salary earners
D. increases the value of a country’s exports.
6. What could be the opportunity cost of a nuclear power station?
A. the running costs of the power station
B. a coal-fired power station
C. the current value of the power station
D. the cost of building the power station.
7. The diagram below shows a production possibility curve for maize and cotton.
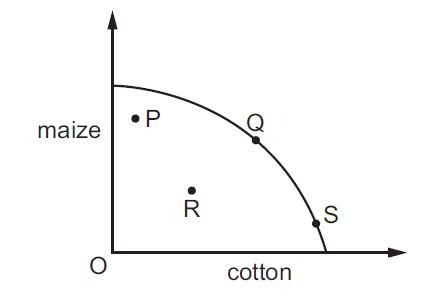
Bad weather causes a poor harvest for both crops. Which movement could be used to represent this change?
A. P to R B. Q to R C. S to Q D. S to R.
8. The market for a good was in equilibrium. A change occurred which resulted in a new equilibrium with a higher price for the good and a lower quantity traded.
What change would have caused this?
A. the demand curve moved to the left
B. the demand curve moved to the right
C. the supply curve moved to the left
D. the supply curve moved to the right.
9. A demand curve shows the relationship between the quantity demanded and ________
A. a change in income
B. consumer tastes
C. the supply of the product
D. the price of the product.
10. A government subsidises the production of pineapples. This is likely to _______
A. increase the price of pineapples
B. raise the costs of supplying pineapples
C. raise revenue for the government
D. cause the supply of pineapples to increase at every price.
11. What indicates the existence of external costs in an economy?
A. An international trade deficit has caused the country to be in debt.
B. National companies have borrowed from foreign investors.
C. Private costs of production are less than social costs.
D. Private costs of production are more than social benefits.
12. What might be a disadvantage to a trade union when arguing for an increase in its members’ pay?
A. an increase in imports of a cheaper, similar product
B. the closure of a local training college resulting in fewer potential workers
C. the development of a new and profitable brand of the company’s product
D. the development of new techniques that increase productivity.
13. A German car manufacturer decided to produce its cars in a factory in China. What would not be a reason why they might have chosen to do this?
A. cheaper wage costs in China
B. the availability of raw materials
C. to gain external economies from skilled labour in China
D. to increase Germany self-sufficiency.
14. A government removed the quota on goods imported into the country.
What is the most likely result of this?
A. a decrease in demand for domestic production
B. a decrease in domestic unemployment
C. a decrease in exports
D. a decrease in the balance of trade deficit.
15. A modern corporation is owned by ________
A. debenture holders B. ordinary shareholders C. preference shareholders D. creditors.
16. One of the most important factors that should be considered in the location of an industry is _________
A. nearness to the financial centre
B. assured patronage by government functionaries
C. availability of inputs and market
D. availability of adequate security.
17. What is the term used to describe a policy aimed at promoting the local production of goods which are usually imported?
A. deregulation B. import substitution C. tariff reduction D. backward integration.
18. Progressive tax structure is designed to ___________
A. take more from the income of the poor
B. take more from the income of the rich
C. take equal proportion of income from both the rich and the poor
D. reduce the problems emanating from tax imposition.
19. Which of the following best describes the production function?
A. it indicates the best output to produce
B. it relates naira inputs to naira outputs
C. it relates physical outputs to physical inputs
D. it indicates the best way to combine factors to produce any given output.
20. Which of the following reward is associated with entrepreneurship as a factor of production?
A. salaries B. profits C. interest D. rents.
21. In a market economy, the question of what, how and for whom to produce are solved by the ________
A. elected representative of the people
B. planning committee
C. price mechanism
D. government.
22. At any given level of output, a firm’s total variable cost equals ________
A. total cost less marginal cost
B. total cost less total fixed cost
C. total cost less average cost
D. average variable cost and marginal variable cost.
Age groups (years) Distribution (%)
Above 60 30
15 – 60 45
0 – 14 25
23. From the above, the estimated dependency ratio of the population shown above is _______ A. 11: 9 B.9: 11 C. 7: 3 D. 3: 7
23. Which of the following factors is NOT responsible for the rural /urban drift in Nigeria?
A. the infrastructural facilities in the cities
B. declining fertility of rural farmlands
C. rural electrification programme
D. higher living standards in urban areas.
24. The necessity of choice is due to the fact that _______
A. human wants are inelastic
B. customers like to maximize satisfaction
C. resources are abundant
D. consumers are selective.
25. What is meant by labour supply?
A. number of people in the working population
B. the number of men and hours they work
C. number of hours during which the middle-aged persons work
D. the number of workforces multiplied by the hours they worked.
26. Any payment to a factor of production in excess of what is necessary to keep its present employment is known as ________
A. real income B. profit C. economic rent D. real wage
27. The market where there are many differentiated products is called ______
A. monopoly B. perfect competition C. monopolistic competition D. Oligopoly.
28.
PS: Once again, there is nothing like Neco Economics expo. Do not fall victim to scammers online trying to obtain money from you with fake promises of having access to live question paper before the exam. What we have on this page are likely exam questions from Neco economics past questions and answers to serve as a revision guide.
Keep following, more questions and answers will be added soon.
