2025 WAEC Biology Answers and Questions Released.
The Waec biology answers 2025 objective and essay questions are now available. The West African Examination Council, WAEC Biology exam paper will be written on Thursday, 23rd May 2024.
The Waec Biology 2 (Essay) paper will start by 9:30 am and will last for 1hr 40 mins while the Biology 1 (Objective) exam will commence at 11:10 am and will last for 50 mins.
In this post, we will be posting samples of the waec biology 2023 questions for candidates who will participate in the examination from past questions. There is nothing like Waec Biology Expo 2024 online. 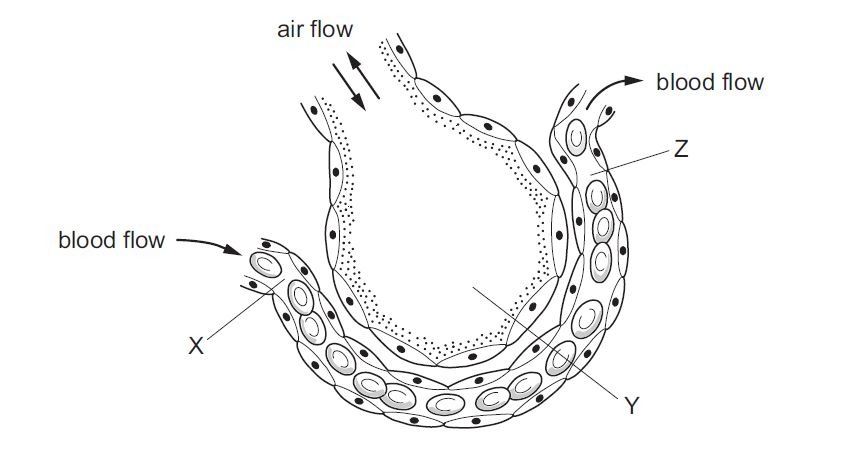
WAEC Biology Answers 2024.
Section B [Essay] Answer any FOUR questions.
Write your answers on the answer booklet provided.
1. a. (i) List three characteristics of living organisms.
(ii) Explain briefly the characteristics listed in 1(a) (i) above.
(b) In a tabular form, state four differences between plants and animals.
(c) (i) Name one organism that exhibits both plant and animal features.
(ii) State four animal features and two plant features possessed by the organism named in 1(c)(i)
ANS:
1.a (i) and (ii) Characteristics of living Organisms…
Movement; Living things change the position of the whole body/parts of the body;
from one place to another; in search of food/shelter/mates, etc.
Excretion; This involves the removal/getting rid of waste products of cell metabolism; metabolic wastes are poisonous if allowed to accumulate.
Respiration; This is the breakdown/burning of food substances; by aerobic/anaerobic respiration; to release energy needed for all processes of life.
Reproduction; This is the ability of living organisms to produce new individuals of their own kind; this ensures the continuity of the species of an organism.
Irritability; Response/reaction of organisms; towards changes in the environment; to ensures survival.
Nutrition; The process involved in obtaining/manufacturing food; can be autotrophic/heterotrophic; and utilizing it for growth and maintenance/life processes.
Growth; This is the irreversible increase; in size and weight of an organism; which leads to complexity and maturation.
Competition; Ability of organisms to struggle; for all necessity of life; to survive in their environment.
Adaptation; Ability of organisms to adjust; to changes in environment; for survival.
2. a. What is photosynthesis?
b. List: (i) four external factors;
(ii) two internal factors; that affect the rate of photosynthesis.
c. (i) List the major products of the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis.
(ii) State the importance of each of the products listed in 2(c) (i) above.
d. (i)Explain why there are no green plants at the lower depths of some lakes.
(ii) State why decomposers are important to flowering plants.
3. (a) Explain the following terms: (i) disease; (ii) symptoms of diseases
(b) (i) List two physical and two chemical barriers that prevent pathogens from penetrating the body of an organism.
(ii) Explain how vaccination protects the body from contracting infectious diseases.
(c) Distinguish between an antibody and an antigen.
(d) Name the causative agents of: (i) Malaria; (ii) Cholera; (iii) AIDS.
4. (a) (i) What is excretion?
(ii) List the excretory organs in humans and name one waste product excreted by each organ.
(b) How does the mammalian kidney function as an excretory organ?
(c) Name the excretory organs in (i) insects; (ii) earthworms.
5. (a) (i) What is conservation?
(ii) State six factors responsible for the decline of the abundance and variety of wildlife.
(b) Outline six ways in which the government can improve the situation in 5(a) (ii) above.
(c) (i) What is Eutrophication?
(ii) State two causes of eutrophication.
6. (a) Describe the carbon cycle. (b) State the functions of: (i) nitrogen fixing bacteria; (ii) nitrifying bacteria; (iii) denitrifying bacteria; in nature.
ANS: (a) Carbon occurs in the air/ atmosphere/as carbon dioxide/dissolved in the oceans /seas/ water bodies, and is circulated continuously; through the activity of microorganisms /decay bacteria/ saprophytic organisms /fungi; which decompose the dead organisms; plants /animals release carbon dioxide and water; the carbon dioxide released increases the concentration of carbon in the atmosphere /ocean/ sea /water bodies; this is further increased by respiration in plants and animals;
combustion of wood/ coal/ oil/ fuel; some of the excess carbon dioxides is absorbed by the sea /water bodies and also used by plants in photosynthesis; organisms in seas /oceans /water bodies release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere/ water.
(b) Functions of – (i) Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria; Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the nodules of legumes; those living freely in the soil; convert atmospheric nitrogen; into ammonia /ammonium compounds.
(ii) Nitrifying Bacteria; They live freely in the soil; oxidize/breakdown the ammonium compounds; to nitrites; which are then oxidized by others/ Nitrobacter/ named bacteria; to nitrates.
(iii) Denitrifying Bacteria; They live freely in the soil; these break down/ oxidize ammonium compounds; into nitrogen; and oxygen; which is released into the atmosphere.
7. (a) (i) What is a gene?
(ii) Differentiate between the terms genotype and phenotype.
(b) Explain the following terms: (i) hybrid; (ii) pure breeding; (iii) nucleotide.
(c) In garden pea seeds, a smooth seed coat is dominant over a rough seed coat. With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the result expected if a homozygous rough pea is crossed with a smooth seed coat plant whose parent were rough-coated.
8. (a) (i) Describe epigeal germination of a seed.
(ii) In a tabular form, state three differences between epigeal germination and hypogeal germination.
(b) (i) What is seed dormancy?
(ii) State three ways by which dormancy in seeds can be broken.
(c) State six advantages of using contraceptives in human populations.
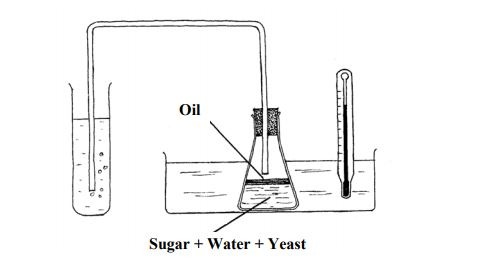
9. 
WAEC Biology Objective Questions 2024.
Section A [Objectives] Answer ALL questions.
Shade your answers on the answer booklet provided.
1. Where are most nitrogen compounds excreted from humans?
A. kidneys B. liver C. rectum D skin.
2. A motor neurone transmits impulses from A muscle to the spinal cord. B receptor to muscle. C receptor to the spinal cord. D spinal cord to muscle.
3. In which order does light pass through these structures in the eye?
A. cornea → aqueous humour → lens → vitreous humour → retina
B. cornea → vitreous humour → lens → aqueous humour → retina
C. lens → aqueous humour → cornea → vitreous humour → retina
D. lens → vitreous humour → cornea → aqueous humour → retina.
4. A person with Down’s syndrome is born with 47 chromosomes in each cell, instead of 46. What could cause this?
A. A mutation happened during the production of the egg cell.
B. More than one sperm fused with the egg at fertilisation.
C. Radiation caused a change in the structure of a gene in the father’s sperm.
D. The mother was exposed to harmful chemicals while she was pregnant.
5. A red-flowered plant is crossed with a white-flowered plant. All the offspring have red flowers. What is the genotype of these offspring?
A. RR and Rr
B. RR only
C. Rr only
D. rr only.
6. A plant has flowers whose anthers mature and fall off before the stigma is fully developed. What will this prevent?
A. cross-pollination B. insect-pollination C. self-pollination D. wind-pollination.
7. The cell wall of a plant cell is removed using an enzyme. What would happen if this cell is then placed in distilled water?
A. It would take longer for the cell to become turgid.
B. Proteins in the cytoplasm would leave through the cell membrane.
C. The cell would become smaller as water passes out.
D. The cell would burst as water moves into it.
8. Some organisms live at the bottom of the seas where it is very dark. To synthesise glucose, they use energy from chemicals in the very hot water that comes out of volcanoes. What is a distinguishing feature of these organisms?
A. Their enzymes are easily denatured by heat.
B. They do not need carbon dioxide.
C. They do not need to be green.
D. They obtain energy only as carnivores.
9. Under which set of conditions will the transpiration rate of a well-watered plant be fastest?
A. a cool, dry, windless day
B. a cool, rainy, windy day
C. a hot, dry, windy day
D. a hot, rainy, windy day.
10. Why is glucose found in the urine of diabetics?
A. increased uptake and use of glucose by the body cells
B. not enough glucose in the blood is converted to glycogen
C. stored fats in the body are being oxidized
D. too much glucose is absorbed by the kidney cells.
11. Which bones form a joint at the shoulder?
A. humerus and scapula B. humerus and ulna C. radius and ulna D. radius and scapula.
12. Which sequence describes the flow of energy in an ecosystem?
A. carnivore → herbivore → plant → Sun
B. plant → herbivore → carnivore → Sun
C. Sun → carnivore → herbivore → plant
D. Sun → plant → herbivore → carnivore.
13.
PS: Once again, there is nothing like the Waec biology expo. Do not fall victim to scammers online trying to obtain money from you with fake promises of having access to a live question paper before the exam. What we have on this page are likely exam questions from Waec biology past questions and answers to serve as a revision guide.
Keep following, more questions and answers will be added soon.
